Aluminum PCB
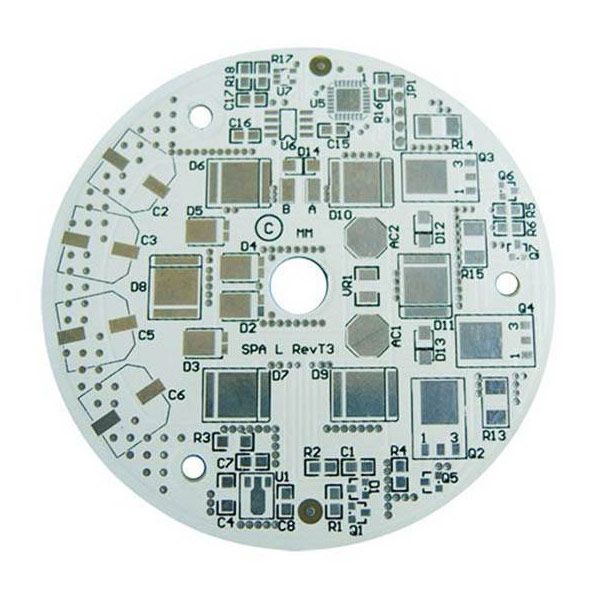
What is Aluminum PCB?
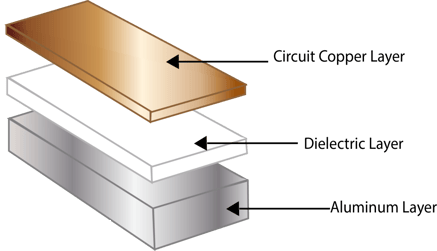
Aluminum PCB is a kind of metal based copper clad laminate with good heat dissipation function. Generally, the single sided aluminum PCB is composed of three layers: circuit layer (copper foil), thermal conductive insulation layer and metal base layer. For high-end use, there are also double-sided aluminum boards, the structure is circuit layer, insulation layer, aluminum base, insulation layer, circuit layer. Very few applications are multi-layer boards, which can be made of ordinary multilayer boards, insulation layer and aluminum base.
LED aluminum substrate is the circuit board whose material is aluminum alloy, because the LED heat is large, so the circuit board for LED lamps is generally aluminum substrate, which can conduct heat fast.
Compared with the traditional FR-4, the aluminum substrate can reduce the thermal resistance to the minimum, so that the aluminum substrate has excellent thermal conductivity; compared with the thick film ceramic circuit, its mechanical properties are excellent. Compared with the traditional FR-4, the aluminum substrate can minimize the thermal resistance and make the substrate excellent. Compared with the thick film ceramic circuit, its mechanical properties are excellent. Aluminum substrate is a kind of copper clad laminate with good heat dissipation function.
How are aluminum PCBs made?
Applications of Aluminum PCBs
Flexible Aluminum PCBs
Hybrid Aluminum PCBs
In a ‘Hybrid’ IMS construction a “Sub-assembly” of a non-thermal material is processed independently and then Amitron Hybrid IMS PCBsbonded to the aluminum base with thermal materials. The most common construction is a 2-Layer or 4-Layer Sub-assembly made from conventional FR-4. Bonding this layer to an aluminum base with thermal dielectrics can help dissipate heat, improve rigidity and act as a shield. Other benefits include:
- Less costly than a construction of all thermally conductive materials
- Provides superior thermal performance over a standard FR-4 product
- Can eliminate costly heat sinks and associated assembly steps
- Can be used in RF applications where a surface layer of PTFE is desired for its’ loss characteristics.
- Use of component windows in the aluminum to accommodate through-hole components. This allows connectors and cables to pass connections through the substrate while the solder fillet creates a seal without the need for special gaskets or other costly adapters.
Through-hole Aluminum PCBs
In the most complex constructions a layer of aluminum can form a ‘Core’ of a multilayer thermal construction. The aluminum is pre-drilled and back-filled with dielectric prior to lamination. Thermal materials or sub-assemblies can be laminated to both sides of the aluminum using thermal bonding materials. Once laminated, the completed assembly is thru-drilled similar to a conventional multilayer PCB. The plated through holes pass through the clearances in the aluminum to maintain electrical insulation. Alternatively a Copper core can allow both direct electrical connections as well as with insulated through holes.
Multilayer Aluminum PCBs
Common in the high performance power supply market, multilayer IMS PCBs are made from multiple layers of thermally conductive dielectrics. These constructions have one or more layers of circuitry buried in the dielectric with blind vias acting as either thermal vias or signal vias. While more expensive and less efficient at transferring heat as a single layer designs, they provide a simple and effective solution for heat dissipation in more complex designs.